What Is a Proxy Server? Definition, Uses & More
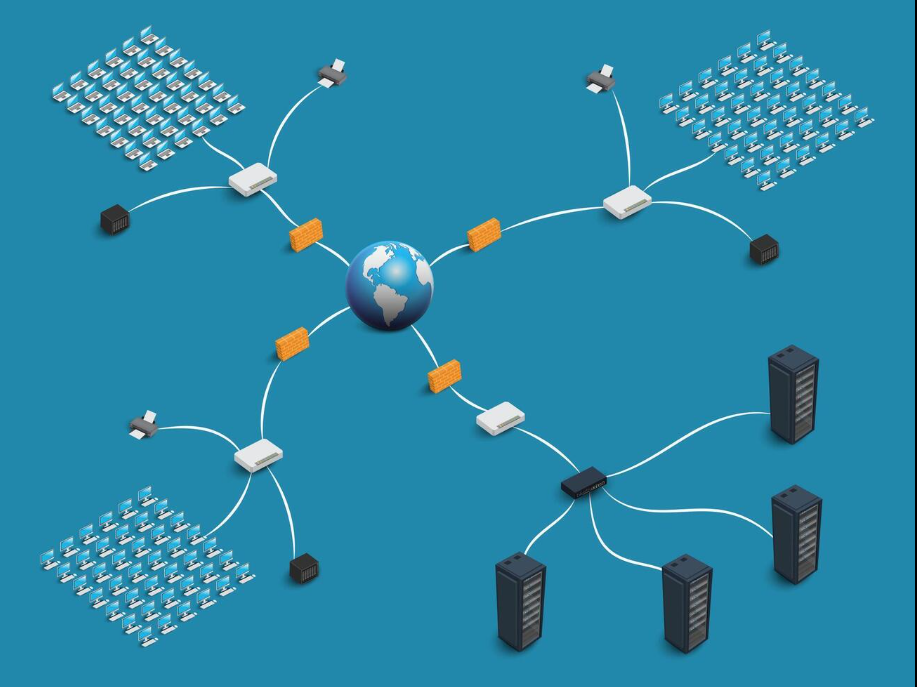
A proxy server is an intermediary that sits between your device and the internet. It helps process requests and responses between you and websites or online services. When you use a proxy, your internet traffic is sent to the proxy server first. The proxy then forwards that traffic to the destination and sends the response back to you.
This extra step offers a range of benefits. Proxies can hide your IP address, improve browsing speed, filter content, and increase security. No matter if you're using the internet at home, in a business setting, or through a public network, proxies can help manage how you access online resources.
Why proxy servers matter
Proxy servers are widely used in homes, schools, offices, and data centers. They are helpful for several reasons:
-
They improve privacy by hiding your real IP address.
-
They allow access to restricted or geo-blocked content.
-
They help businesses monitor and control internet use.
-
They can cache data to improve website loading times.
-
They offer an extra layer of protection against online threats.
As internet usage grows and cyber threats become more common, proxies offer a simple yet powerful tool to manage online access and protect user data.
How proxy servers work
When you visit a website without a proxy, your request goes directly from your device to the site’s server. The website then responds to your device using your IP address.
With a proxy, the process looks different:
-
You enter a web address in your browser.
-
Your request is sent to the proxy server instead of directly to the website.
-
The proxy forwards your request to the website using its address.
-
The website sends its response back to the proxy.
-
The proxy sends the final data to your device.
During this process, the proxy can modify the data, filter content, block ads, or store a copy of frequently requested pages to load them faster.
Types of proxy servers
There are several types of proxy servers, each serving a specific function. Here are the most common ones:
-
Forward proxy - This is the most common type. It works for individual users or organizations to access the internet through a proxy. It hides the user's IP and filters requests.
-
Reverse proxy - Used by web servers, a reverse proxy takes requests from the internet and forwards them to a group of servers. It helps manage traffic, improve speed, and add security.
-
Transparent proxy - This type does not hide the fact that it’s a proxy. It is often used in schools or offices for monitoring and content filtering. Users may not even know they’re using it.
-
Anonymous proxy - This proxy hides your IP address but reveals that it is a proxy. It’s used when privacy is important but transparency is still acceptable.
-
High anonymity proxy (elite proxy) - This type hides your IP address and doesn’t identify itself as a proxy. It offers a high level of privacy and is used in secure or anonymous browsing.
-
Distorting proxy - This kind of proxy hides your IP address and sends a fake IP address instead. It’s useful for bypassing geo-restrictions.
-
SOCKS proxy - SOCKS proxies work at a lower level and can handle any kind of traffic, such as emails, video streaming, and torrents. They are slower but more flexible.
-
Web proxy - This is a proxy that you access through a web browser. No software setup is needed. Just go to a proxy website, enter the URL you want, and browse anonymously.
Common uses of proxies
Proxies serve many purposes across different industries and user types. Here are some of the most popular uses:
-
Privacy and anonymity: Hide your IP address while browsing the web.
-
Accessing restricted content: Bypass geo-blocks or network restrictions to access websites, services, or content unavailable in your region.
-
Security: Prevent attackers from reaching your device directly by hiding your identity.
-
Content filtering: Used in schools and offices to block certain websites.
-
Speed and bandwidth control: Caching can store copies of websites, speeding up access for multiple users.
-
Load balancing: In web services, reverse proxies distribute traffic across multiple servers.
-
Monitoring and logging: Businesses use proxies to track internet usage and ensure compliance with company policies.
Benefits of using a proxy server
Here’s why people and organizations use proxies:
-
Increased privacy: Your real IP is hidden, making it harder for websites or trackers to identify you.
-
Improved security: Proxies can block access to dangerous sites or ads, helping prevent malware infections.
-
Better speed: Cached content loads faster, especially in shared networks like offices or schools.
-
Bypass restrictions: Access websites or services blocked by network administrators or governments.
-
Manage internet use: Businesses can set limits, filter content, or monitor activity.
What Are Anonymous Proxy Servers?
Anonymous proxy servers are those that hide your real IP address from the websites you visit, helping you browse the internet without revealing your identity or location. An anonymous proxy routes your web traffic through a different IP address when you connect to the internet.
The website you visit sees the proxy server’s IP—not yours—making it harder to trace your activity back to you. Anonymous proxy servers are useful for basic privacy and content access, but for stronger security, consider using a VPN instead.
Risks and things to watch out for
While proxies offer many benefits, they also have some risks if not set up properly:
-
Untrustworthy providers: Free proxies may log your activity or sell your data.
-
No encryption: Basic proxies don’t encrypt your data, making it vulnerable to interception.
-
Slower speeds: Some proxies, especially overloaded or poorly managed ones, can slow down your connection.
-
Compatibility issues: Some websites block traffic from known proxies.
To minimize risks, always use trusted proxy services or configure your own with proper security settings. Avoid entering sensitive information like passwords when using public proxy servers.
Proxy vs. VPN: What’s the difference?
While both proxies and VPNs hide your IP address, they work differently:
-
Proxies redirect specific traffic (like your browser).
-
VPNs redirect all internet traffic from your device.
-
VPNs also encrypt data, offering stronger security.
If your goal is simply to hide your IP address while browsing, using a proxy is usually sufficient. For more protection, especially on public Wi-Fi, a VPN is a better choice.
How to get a proxy
Here’s a simple guide on how to get a proxy:
-
Choose a type of proxy
-
Sign up and select a plan
-
Get proxy details
-
Set up the proxy on your device or app
-
Test the proxy
How to set up a proxy
Setting up a proxy is usually simple. Most operating systems and browsers allow manual proxy configuration.
On Windows:
-
Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Proxy.
-
Enter the proxy server address and port number.
On macOS:
-
Go to System Preferences > Network > Advanced > Proxies.
-
Enable the desired proxy and enter the server details.
You can also use browser extensions or third-party proxy software if you need more control or want quick switching between proxy servers.
What is the difference between a business and consumer proxy?
The main difference between a business proxy and a consumer proxy lies in their purpose and performance.
Business proxies are designed for companies that need reliable, scalable, and secure solutions for tasks like data scraping, ad verification, and market research. They offer advanced features such as dedicated IPs, better speed, higher uptime, and customer support.
Consumer proxies are intended for personal use, such as anonymous browsing or accessing geo-restricted content. They are generally simpler and less expensive and may have limited features or lower performance compared to business-grade services.
Final thoughts
A proxy server is a valuable tool for privacy, control, and efficiency. It helps manage how you connect to the internet, hides your identity, and can speed up or secure your online experience. No matter if you’re trying to access content abroad, protect sensitive data, or manage a network, proxies are versatile and useful.
To make the most of your proxy setup, you need reliable networking equipment. TP-Link offers a wide range of high-performance routers, access points, and network management tools that support proxy configurations and enhanced security features.
If you're managing a home network or running a small business, TP-Link products help you stay private, protected, and in control.
Proxy Server FAQs
Should You Use a Proxy Server Instead of a VPN?
Use a proxy for simple tasks like hiding your IP. Use a VPN for secure, private, and encrypted internet access.
Are proxy servers and VPNs the same?
No. While both hide your IP, VPNs encrypt all your traffic, offering stronger security. Proxies only affect specific apps or browsers.
Are proxy servers safe to use?
Paid and reputable proxies are generally safe. However, free proxies can be risky and may track your data or inject ads.
Can I use a proxy on my phone?
Yes. Most smartphones allow proxy configuration in Wi-Fi settings, and some apps support proxy use directly.
Can proxies improve internet speed?
In some cases, yes—especially caching proxies, which store frequently accessed content. However, proxies can also slow down speed if overloaded or poorly configured.


_20240830071121x.jpg)
_20240830062251t.jpg)
_20240830055723o.jpg)