Archer A10 V1 User Guide
- About This Guide
- Chapter 1 Get to Know About Your Router
- Chapter 2 Connect the Hardware
- Chapter 3 Log In to Your Router
- Chapter 4 Set Up Internet Connection
- Chapter 5 Set Up the Router as an Access Point
- Chapter 6 TP-Link Cloud Service
- Chapter 7 Guest Network
- Chapter 8 Parental Controls
- Chapter 9 QoS
- Chapter 10 Network Security
- Chapter 11 NAT Forwarding
- Chapter 12 VPN Server
- Chapter 13 Customize Your Network Settings
- Chapter 14 Manage the Router
- FAQ
- Authentication
Chapter 14 Manage the Router
This chapter will show you the configuration for managing and maintaining your router.
It contains the following sections:
•Test the Network Connectivity
•Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
•Set the Router to Reboot Regularly
•Change the Administrator Account
System time is the time displayed while the router is running. The system time you configure here will be used for other time-based functions like Parental Controls. You can choose the way to obtain the system time as needed.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Time Settings.
•To get time from the Internet:
1.Click Get from GMT.
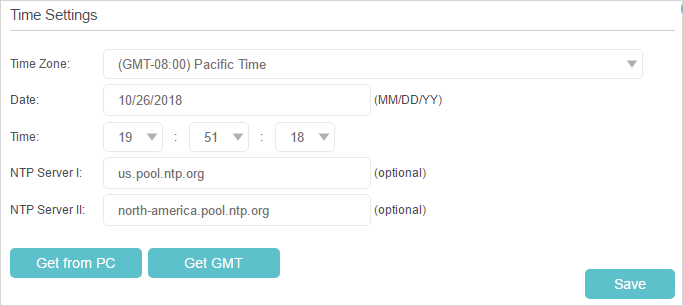
2.Select your local Time Zone from the drop-down list.
3.(Optional) Enter the IP address of the NTP Server I or NTP Server II, and the router will get the time from the NTP Server automatically. In addition, the router has some common built-in NTP Servers that will synchronize automatically once it connects to the internet.
4.Click Save.
•To get time from PC
1.Click Get from PC.
2.The current system time and date of your PC will display on the interface.
3.Click Save.
Tips: Make sure the time on your PC is correct if you want to get the PC’s system time.
•To manually set the time:
1.Set the current Date (In MM/DD/YYYY format).
2.Set the current Time (In HH/MM/SS format).
3.Click Save.
•To set up Daylight Saving Time:
1.Select Enable Daylight Saving Time.
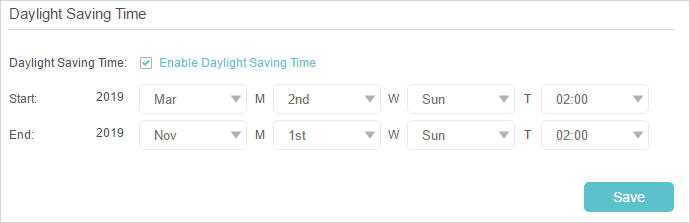
2.Select the correct Start date and time when daylight saving time starts at your local time zone.
3.Select the correct End date and time when daylight saving time ends at your local time zone.
4.Click Save.
2. Test the Network Connectivity
Diagnostics is used to test the connectivity between the router and the host or other network devices.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Diagnostics.
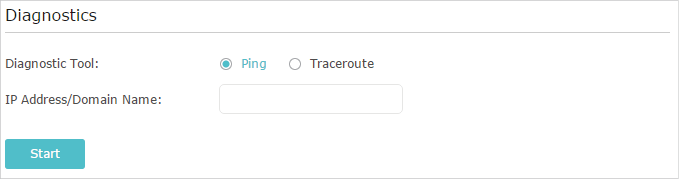
3.Enter the information with the help of page tips:
1 )Choose Ping or Traceroute as the diagnostic tool to test the connectivity;
•Ping is used to test the connectivity between the router and the tested host, and measure the round-trip time.
•Traceroute is used to display the route (path) your router has passed to reach the tested host, and measure transit delays of packets across an Internet Protocol network.
2 )Enter the IP Address or Domain Name of the tested host.
4.Click Start to begin the diagnostics.
Tips:
Click Advanced, you can modify the ping count, ping packet size or the Traceroute Max TTL. It’s recommended to keep the default value.
The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Ping.
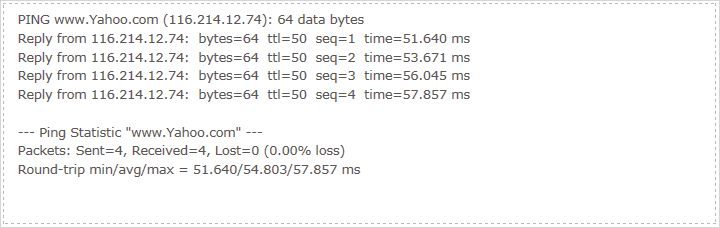
The figure below indicates the proper connection between the router and the Yahoo server (www.Yahoo.com) tested through Traceroute.

TP-Link aims at providing better network experience for users.
We will inform you throught the web management page if there’s any update firmware available for your router. Also, the latest firmware will be released at the TP-Link official website www.tp-link.com, and you can download it from the Support page for free.
Note:
•Backup your router configuration before firmware upgrade.
•Do NOT turn off the router during the firmware upgrade.
3.1. Online Upgrade
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.When the latest firmware is available for your router, the update icon will display in the top-right corner of the page. Click the icon to go to the Firmware Upgrade page.
Alternatively, you can go to Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade, and click Check for upgrade to see whether the latest firmware is released.

3.Focus on the Online Upgrade section, and click Upgrade.
4.Wait a few minutes for the upgrade and reboot to complete.
Tips:
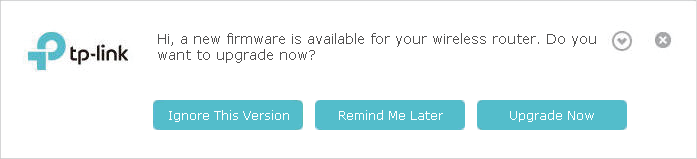
If there’s a new and important firmware update for your router, you will see the notification (similar as shown below) on your computer as long as a web browser is opened. Click Upgrade now, and log into the web management page with the username and password you set for the router. You will see the Firmware Upgrade page.
3.2. Local Upgrade
1.Download the latest firmware file for the router from www.tp-link.com.
2.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
3.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Firmware Upgrade.
4.Focus on the Device Information section. Make sure the downloaded firmware file is matched with the Hardware Version.
5.Focus on the Local Upgrade section. Click Browse to locate the downloaded new firmware file, and click Upgrade.
6.Wait a few minutes for the upgrade and reboot to complete.
3.3. Restore Interrupted Upgrade after Power Failure
If your router cannot start up after an upgrade interruption due to power failure, follow the steps below to restore the interrupted upgrade. Otherwise, your router cannot work again.
1.Make sure you have the latest firmware file in your computer. If not, try another way to connect your computer to the Internet and download the latest firmware file from www.tp-link.com.
2.Connect your computer to the router with an Ethernet cable.
3.Visit 192.168.0.1 and you will see the following upgrade page.
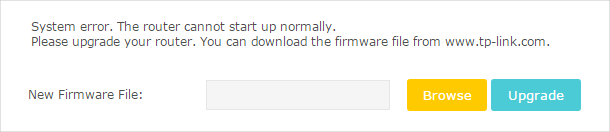
4.Click Browse and select the downloaded firmware file.
5.Click Upgrade and wait for a few minutes until the router completes the upgrading and restarts.
4. Backup and Restore Configuration Settings
The configuration settings are stored as a configuration file in the router. You can backup the configuration file to your computer for future use and restore the router to a previous settings from the backup file when needed. Moreover, if necessary you can erase the current settings and reset the router to the default factory settings.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Backup & Restore.
•To backup configuration settings:
Click Backup to save a copy of the current settings to your local computer. A ‘.bin’ file of the current settings will be stored to your computer.
•To restore configuration settings:
1.Click Browse to locate the backup configuration file stored on your computer, and click Restore.
2.Wait a few minutes for the restoring and rebooting.
Note: During the restoring process, do not turn off or reset the router.
•To reset the router except your login password and bound TP-Link ID:
1.Click Restore under the Factory Default Restore session.
2.Wait a few minutes for the resetting and rebooting.
Note:
•During the resetting process, do not turn off the router.
•After reset, you can still use the current login password or the TP-Link ID to log in to the web management page.
•To reset the router to factory default settings:
1.Click Factory Restore to reset the router.
2.Wait a few minutes for the resetting and rebooting.
Note:
•During the resetting process, do not turn off or reset the router.
•We strongly recommend you backup the current configuration settings before resetting the router.
5. Set the Router to Reboot Regularly
The Scheduled Reboot feature cleans the cache to enhance the running performance of the router. You can reboot the router manually or set it to reboot regularly.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Reboot.
•To reboot manually
Click Reboot and wait a few minutes for the router to restart.
•To reboot regularly
1.Select Timeout to reboot the router when time is out or select Schedule to set when and how often the router reboots regularly.
2.Click Save.
6. Change the Administrator Account
The account management feature allows you to change your login password of the web management page.
Note:
If you are using a TP-Link ID to log in to the web management page, the account management feature will be disabled. To manage the TP-Link ID, go to Basic > TP-Link Cloud.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and focus on the Account Management section.
3.Enter the old password, then a new password twice (both case-sensitive). Click Save.
4.Use the new password for future logins.
This feature allows you to limit the number of client devices on your LAN from accessing the router by using the MAC address-based authentication.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and complete the settings In Local Management section as needed.
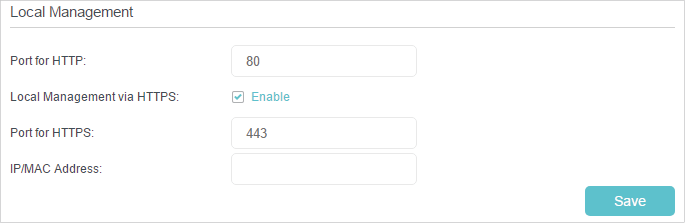
3.Enable Local Management via HTTPS as needed.
4.Keep the Port as the default setting. Enter a valid local IP address or MAC address of the device to be allowed to access the router.
5.Click Save to make the settings effective. Now only the device using the IP address or MAC address you set can manage the router.
Note:
1.The IP address of the local device must be in the same subnet as the router’s LAN IP address.
2.If you want that all local devices can manage the router, just leave the IP/MAC Address field blank.
This feature allows you to control remote devices’ authority to manage the router.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Administration and enable Remote Management.
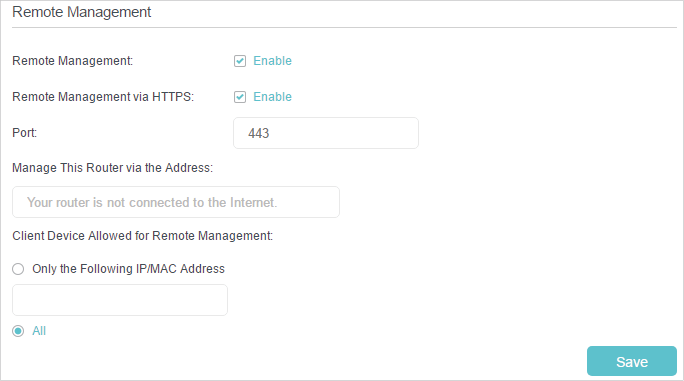
3.Enable Remote Management via HTTPS as needed.
4.Enter the port number to be used to access the router with greater security between 1024 and 65535. The default port number for HTTP is 80 and 443 for HTTPs.
5.If you want a specific device to be allowed to access the router remotely, select Only the Following IP/MAC Address and enter a valid local IP address or MAC address of the device. If you want all devices to be allowed to access the router remotely, select All.
6.Click Save and now you can remotely access and manage the router via the displayed address.
When the router does not work normally, you can save the system log and send it to the technical support for troubleshooting.
•To save the system log in local:
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Log.
3.Choose the type and level of the system logs as needed.
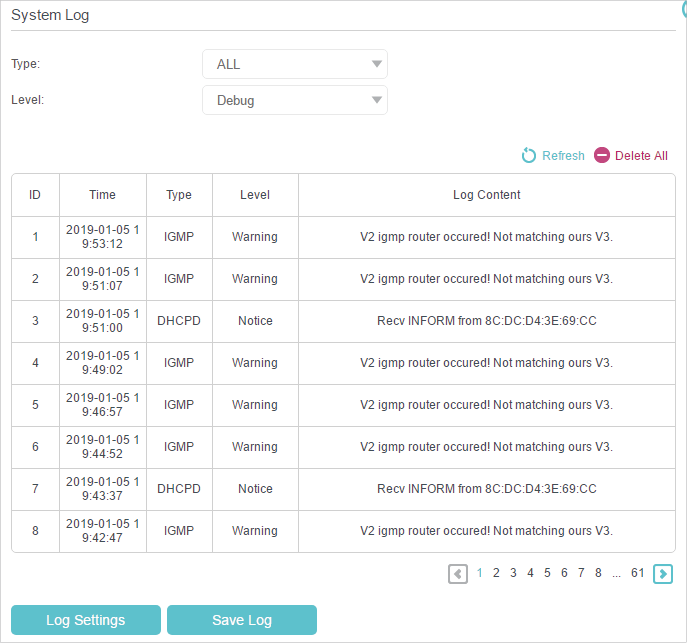
•To view the system logs:
1.Select the log Type. Select ALL to view all kinds of logs, or select a specific type to view the specific logs.
2.Select the log Level and you will see the logs with the specific or higher levels.
3.Click Refresh to refresh the log list.
•To save the system logs:
You can choose to save the system logs to your local computer or a remote server.
Click Save Log to save the logs in a txt file to your computer.
Click Log Settings to set the save path of the logs.
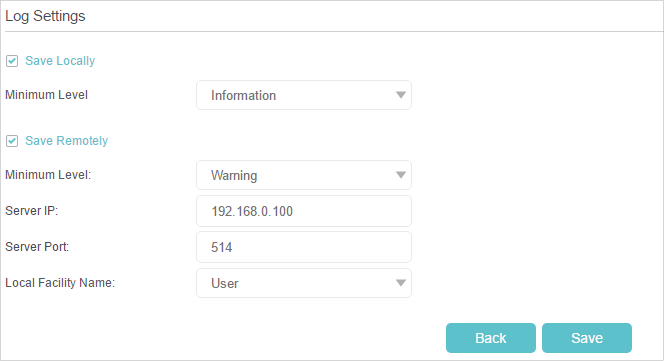
•Save Locally: Select this option to cache the system log to the router’s local memory, select the minimum level of system log to be saved from the drop-down list. The logs will be shown in the table in descending order on the System Log page.
•Save Remotely: Select this option to send the system log to a remote server, select the minimum level of system log to be saved from the drop-down list and enter the information of the remote server. If the remote server has a log viewer client or a sniffer tool implemented, you can view and analyze the system log remotely in real-time.
10. Monitor the Internet Traffic Statistics
The Traffic Statistics page displays the network traffic of the LAN, WAN and WLAN sent and received packets, allows you to monitor the volume of internet traffic statistics.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > Statistics.
3.Enable traffic statistics, and then you can monitor the traffic statistics in Traffic Statistics List section.
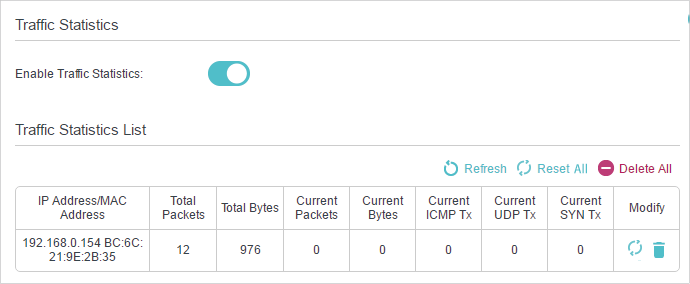
Click Refresh to update the statistic information on the page.
Click Reset All to reset all statistic values in the list to zero.
Click Delete All to delete all statistic information in the list.
Click to reset the statistic information of the specific device.
Click to delete the specific device item in the list.
11.1. Wireless Advanced
You can configure the parameters of traffic transmission rules in wireless networks. It’s recommended to keep the default settings if you are not sure of the proper ones in the case. Click on the management interface to know more about items.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters. Focus on Wireless Advanced section.
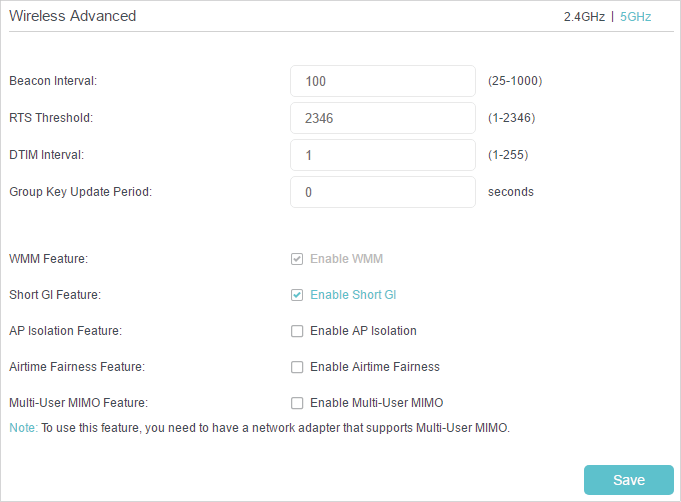
•WMM Feature - It is enabled by default and highly recommended, for the WMM function guarantees the packets with high-priority messages being transmitted preferentially.
•Short GI Feature - It is enabled by default and highly recommended, for it will increase the packet capacity by reducing the GI (Guard Interval) time.
•AP Isolation Feature - If you want to confine and restrict all wireless devices connected to the network from interacting with each other, but still able to access the internet, enable AP Isolation feature.
•Airtime Fairness Feature - This feature allows you to optimize the throughput of each flow. The ATF traffic scheduler uses the per-destination airtime targets to balance airtime usage across flow destinations.
•Multi-User MIMO Feature - Enable to use Multi-User MIMO Feature. Only available for 5GHz.
Note: To use this feature, you need to have a network adapter that supports Multi-User MIMO.
11.2. WDS
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) Bridging feature allows you to bridge a router with an access point to extend the wireless network coverage. The access point should also support WDS Bridging feature.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters. Focus on WDS section.
3.Enable the WDS Bridging feature.
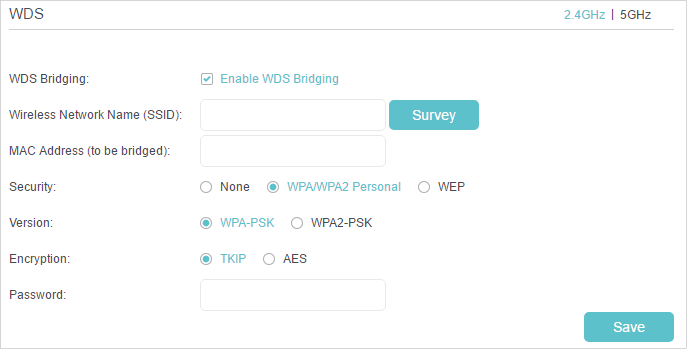
4.Click Survey to scan all available networks and select the network you want to bridge. The SSID (network name) and MAC Address will be automatically populated. You can also manually fill in these parameters.
5.Select a Security type and enter related parameters, which should be the same as the network to be bridged.
6.Click Save.
Note: You need to enable and configure the WDS Bridging feature for the access point as well.
7.Disable DHCP:
1 )Go to Network > DHCP Server.
2 )Deselect Enable DHCP Server and click Save.
Now you can go to Advanced > Status > Wireless to check the WDS status. When the WDS status is Run, it means WDS bridging is successfully built.
The router‘s LEDs indicate router’s activities and status. You can turn on or turn off the LEDs either from the web management page or by pressing the LED button.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters. Focus on LED section.
3.Tick the Night Mode checkbox.
4.Specify a time period in the LED Off Time as needed, and the LEDs will be off during this period.
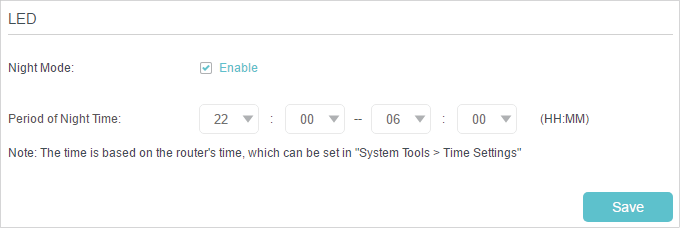
5.Click Save.
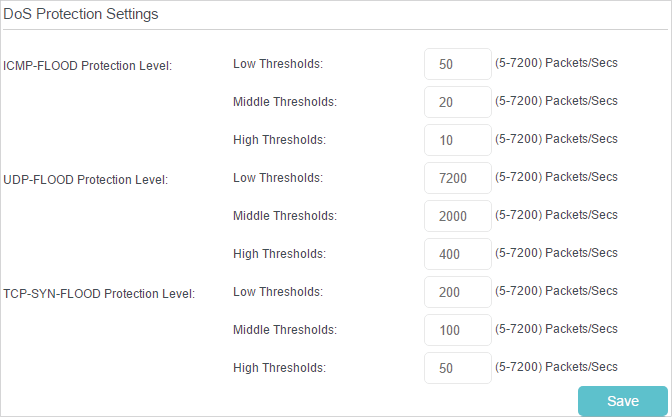
DoS Protection can protect your home network against DoS attacks from flooding your network with server requests.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with your TP-Link ID or the password you set for the router.
2.Go to Advanced > Security > Settings to enable Dos Protection.
3.Go to Advanced > System Tools > System Parameters.
4.Enter a value between 5 and 7200 to trigger the protection immediately when the number of packets exceeds the preset threshold value.