What Is WAN (Wide-Area Network)? A Simple Guide
A Wide-Area Network or WAN is a large network that connects devices and smaller networks (like LANs) across long distances. WANs make it possible for computers and systems in different cities, countries, or even continents to communicate and share data. The internet itself is the biggest and most well-known example of a WAN.
In this guide, we’ll explain what WAN is, how it works, why it’s important, and how it compares to other types of networks like LAN and MAN.
Why WAN Matters
Now that people and businesses are spread across different locations, WANs make global communication and data sharing possible. WANs allow companies to connect their offices in different parts of the world and enable people to access websites, email, and cloud services.
Without WANs, each network would be isolated, and online services like remote work, video calls, cloud backups, and online banking wouldn’t be possible. To put it simply, WANs make the modern internet-connected world work.
How WAN Works
A WAN connects different Local Area Networks (LANs) or other types of networks through routers, switches, and communication links. These links can be established using various technologies, including fiber optic cables, satellite connections, wireless networks, public telephone lines, and undersea cables.
Unlike a LAN that usually belongs to a single organization or household, WANs often use leased lines or public networks to connect over large distances. Internet Service Providers (ISPs), telecom companies, and other infrastructure providers manage these connections.
When you send data over a WAN, it passes through multiple routers and network switches to reach its destination. The path taken depends on routing protocols that determine the most efficient or available route at the time.
Important Features of WAN
WANs have several characteristics that set them apart from smaller networks:
-
Large geographic coverage: WANs can connect users and devices across the world.
-
Multiple network types: A WAN often includes LANs, MANs (Metropolitan Area Networks), and other sub-networks.
-
High latency: Because of the distance, data transmission may experience delays compared to LANs.
-
Public and private ownership: Some parts of a WAN are privately owned (like a company’s internal systems), while others (like the internet backbone) are publicly managed.
-
Scalability: WANs can grow as needed, supporting thousands or even millions of users.
Examples of WAN
There are many examples of WANs in everyday life and business:
-
The Internet: The largest WAN, connecting billions of devices worldwide.
-
Corporate WANs: Large companies use WANs to connect offices, data centers, and remote workers.
-
Banking networks: Banks use WANs to link ATMs, branches, and servers in different locations.
-
Educational institutions: Universities with campuses in different regions connect their networks through WANs.
WAN vs. LAN vs. MAN
Here’s how a WAN compares to other network types:
-
LAN (Local Area Network): Covers a small area like a home or office. It is characterized by its speed, low cost, and ease of management.
-
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Spans a city or large campus. It is larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
-
WAN (Wide-Area Network): Connects networks over large distances. WANs are more complex and require more infrastructure.
Benefits of WAN
WANs offer several important benefits. One of these is global connectivity. They allow users to communicate and access information regardless of their physical location. Whether an employee is traveling overseas or a customer is accessing a cloud-based application, WANs enable seamless global access to data and services.
Centralized data access allows businesses to store their critical data in one place while giving access to users across different sites. This means employees in different offices can access the same files, applications, and tools, leading to more efficient operations and improved collaboration.
Remote work support is another major advantage. WANs enable employees to log in to their company's network securely from anywhere with an internet connection. Business continuity is greatly enhanced through WANs.
These networks can include backup systems and alternate data routes so that operations can continue even if one part of the network goes down. Companies can also use WANs to support disaster recovery sites that take over in case of a failure at the main location, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Challenges of WAN
Despite the benefits, WANs also come with challenges:
-
Latency and speed: Longer distances can slow down communication.
-
Cost: Setting up and maintaining a WAN can be expensive due to equipment and leased lines.
-
Security: Transmitting data over public networks increases the risk of cyber threats.
-
Complexity: Managing a WAN requires skilled IT staff and advanced tools.
To overcome these challenges, organizations often use technologies like:
-
VPN (Virtual Private Network): To secure data sent over public WANs.
-
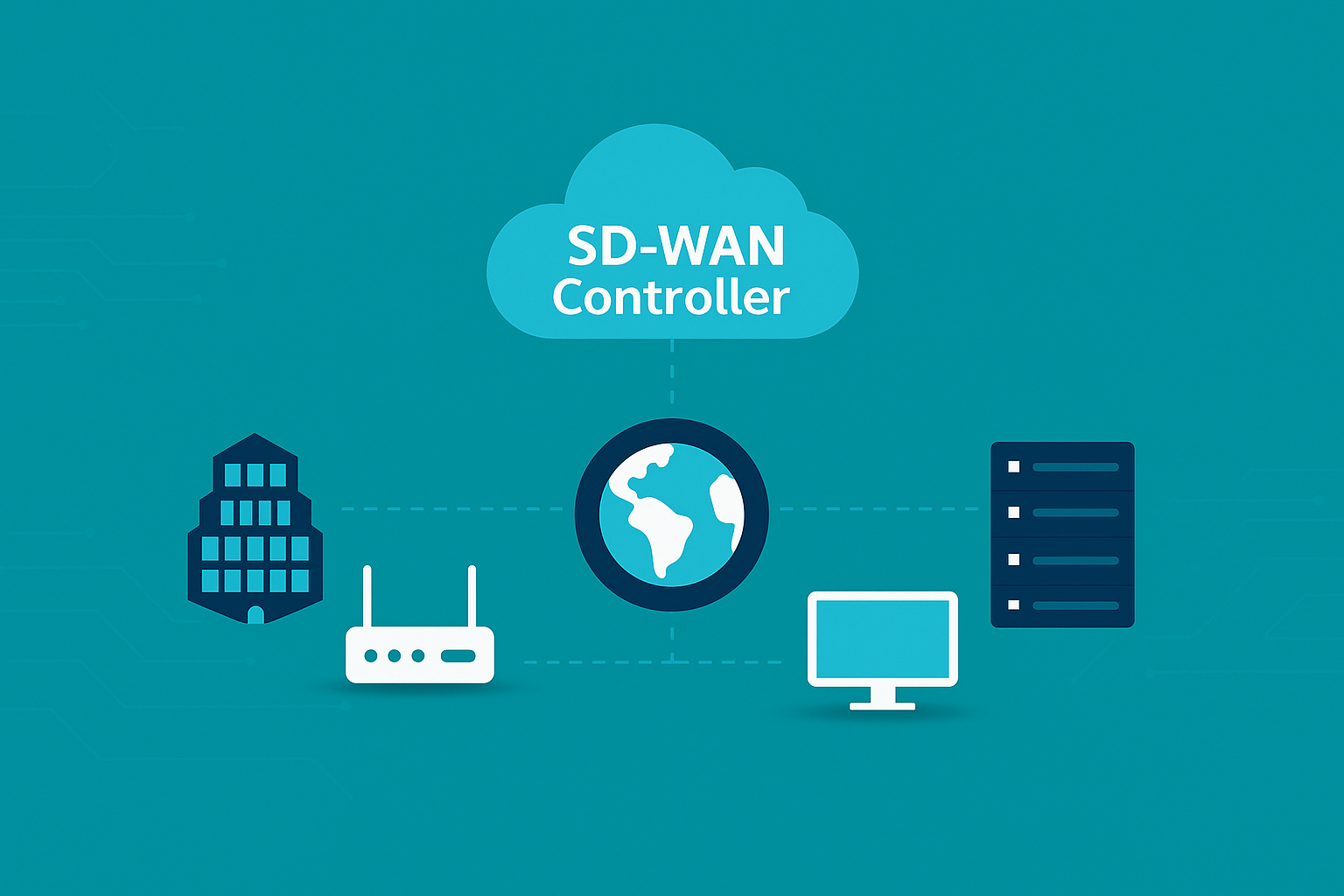
SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN): To manage traffic and improve performance.
-
Firewall and encryption tools: To protect sensitive information.
Types Of WAN Technologies
Here’s a clear breakdown of the main types of WAN (Wide Area Network) technologies, which are used to connect networks across large geographic areas—such as between branch offices, data centers, or remote users:
-
Leased Line: A dedicated point-to-point connection between two locations.
-
MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching): A private, high-performance technique for WAN routing used by service providers.
-
Broadband Internet: Public internet connections (DSL, cable, fiber).
-
4G/5G/LTE Wireless WAN: This technology uses mobile networks to provide WAN connectivity.
-
Satellite WAN: Uses satellites to provide connectivity in remote or rural areas.
-
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network): Digital transmission over traditional telephone lines.
-
Frame Relay: Packet-switching protocol for transmitting data over WAN.
-
SD-WAN (Software-Defined WAN): A modern WAN that uses software to manage multiple connection types (MPLS, broadband, LTE).
How WAN Is Used Today
As cloud computing, mobile workforces, and IoT (Internet of Things) continue to grow, WANs are becoming more important than ever. WANs are used in nearly every industry:
-
Retail: To manage inventory and sales data across branches.
-
Healthcare: For telemedicine, electronic health records, and remote diagnostics.
-
Education: For online classes, remote exams, and access to academic resources.
-
Government: For public services, data sharing, and secure communication between departments.
What is a WAN router?
A WAN router is a type of network device that connects a local area network (LAN)—like the one in your home or office—to a wide area network (WAN), such as the internet or a larger corporate network.
While most consumer routers have basic WAN capabilities (like connecting to your ISP), enterprise-grade WAN routers offer advanced features.
What is WAN optimization?
WAN optimization refers to a set of technologies and techniques designed to improve the performance, speed, and efficiency of data transmission across a Wide Area Network (WAN)—especially between geographically dispersed offices, data centers, or cloud environments.
Final Thoughts
A Wide-Area Network (WAN) connects networks and devices over large distances, making global communication, remote work, and online services possible. Understanding how WANs work can help you better manage your internet use and technology at home or in business.
TP-Link offers networking products that help you build fast, secure, and reliable WAN connections. From enterprise-grade routers to VPN support and SD-WAN-ready solutions, TP-Link gives you the tools to stay connected across long distances.
Check out our collection of WAN-ready networking gear for homes, businesses, and enterprise needs today!