TL-WR940N V6 User Guide
Chapter 6 Configure the Router in Repeater Mode
This chapter presents how to configure the various features of the router working as a Repeater.
It contains the following sections:
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Status. You can view the current status information of the router in Repeater Mode.
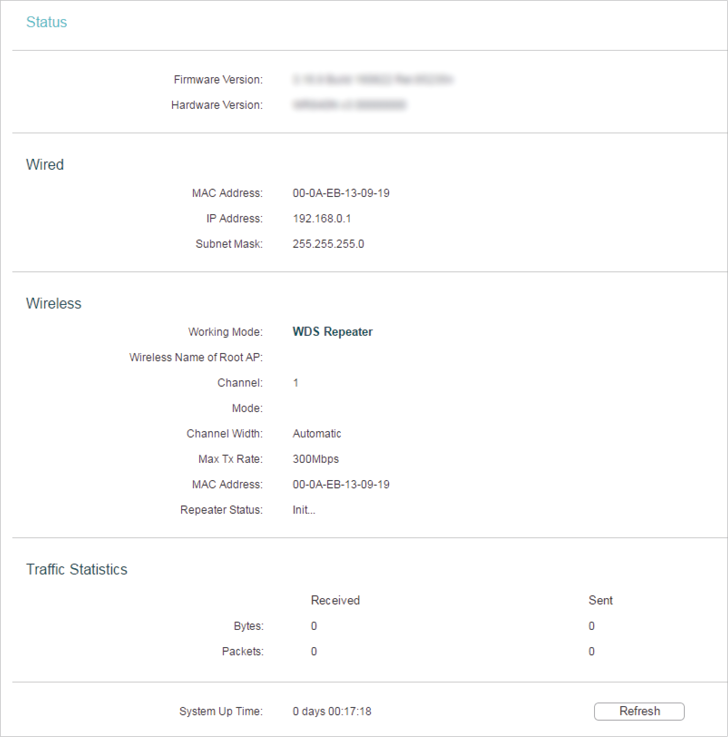
•Firmware Version - The version information of the router’s firmware.
•Hardware Version - The version information of the router’s hardware.
•Wired - This field displays the current settings of the LAN, and you can configure them on the Network > LAN page.
•MAC address - The physical address of the router.
•IP address - The LAN IP address of the router.
•Subnet Mask - The subnet mask associated with the LAN IP address.
•Wireless - This field displays the basic information or status of the wireless function, and you can configure them on the Wireless > Wireless Settings page.
•Working Mode - The current operation mode.
•Wireless Name of Root AP - The SSID of the root router.
•Channel - The current wireless channel.
•Mode - The current wireless working mode.
•Channel Width - The current wireless channel width.
•MAC Address - The physical address of the router.
•Traffic Statistics - The router’s traffic statistics.
•Received (Bytes) - Traffic in bytes received from the WAN port.
•Received (Packets) - Traffic in packets received from the WAN port.
•Sent (Bytes) - Traffic in bytes sent out from the WAN port.
•Sent (Packets) - Traffic in packets sent out from the WAN port.
•System Up Time - The length of the time since the router was last powered on or reset.
Click Refresh to get the latest status and settings of the router.
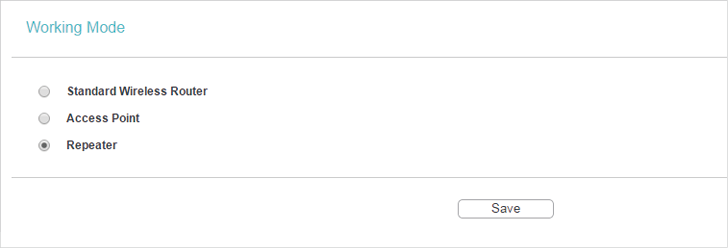
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Working Mode.
3.Select Repeater as needed and click Save.
1. Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Network > LAN.
3.Configure the IP parameters of the LAN and click Save.
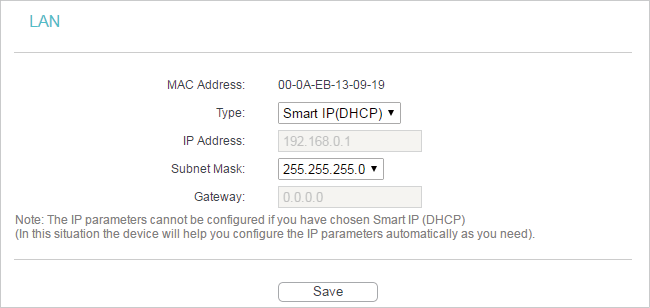
•MAC Address - The physical address of the LAN ports. The value can not be changed.
•Type - Either select Smart IP(DHCP) to get IP address from DHCP server, or Static IP to configure IP address manually.
•IP Address - Enter the IP address in dotted-decimal notation if your select Static IP (factory default - 192.168.0.254).
•Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network. Normally 255.255.255.0 is used as the subnet mask.
•Gateway - The gateway should be in the same subnet as your IP address.
Note:
•If you have changed the IP address, you must use the new IP address to log in.
•If you select Smart IP(DHCP), the DHCP server of the router will not start up.
•If the new IP address you set is not in the same subnet as the old one, the IP Address pool in the DHCP Server will be configured automatically, but the Virtual Server and DMZ Host will not take effect until they are re-configured.
4.1. Wireless Settings
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Wireless Settings.
3.Configure the basic settings for the wireless network and click Save.
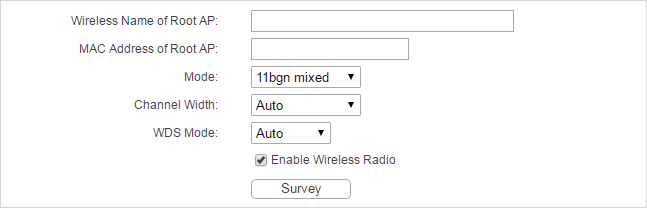
•Wireless Name of Root AP - The SSID of AP that you want to connect to.
•MAC Address of Root AP - The MAC address of AP that you want to connect to.
•Mode - Select the desired mode. It is strongly recommended that you keep the default setting 11bgn mixed, so that all 802.11b/g/n wireless devices can connect to the router.
Note:
If 11bg mixed mode is selected, the Channel Width field will turn grey and the value will become 20M, and cannot be changed.
•Channel Width - Select any channel width from the drop-down list. The default setting is Auto, which can automatically adjust the channel width for your clients.
•WDS Mode -This field determines which WDS Mode will be used. It is not necessary to change the WDS mode unless you notice network communication problems with root AP. If you select Auto, then router will choose the appropriate WDS mode automatically.
•Enable Wireless Router Radio - The wireless radio of the router can be enabled or disabled to allow or deny wireless access. If enabled, the wireless clients will be able to access the router.
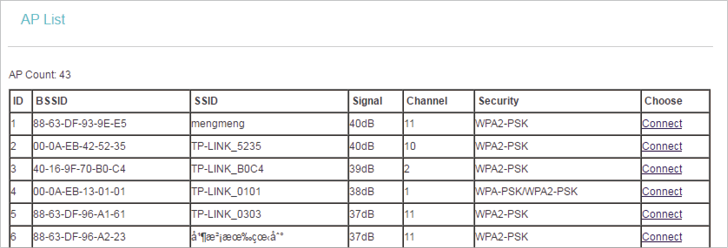
•Survey - Click this button, and the AP List page will appear. Find the SSID of the Access Point you want to connect to, and click Connect in the corresponding row. The target network’s SSID and MAC address will be automatically filled into the corresponding box.
4.2. Wireless Security
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Wireless Security.
3.Configure the security settings of your wireless network and click Save.
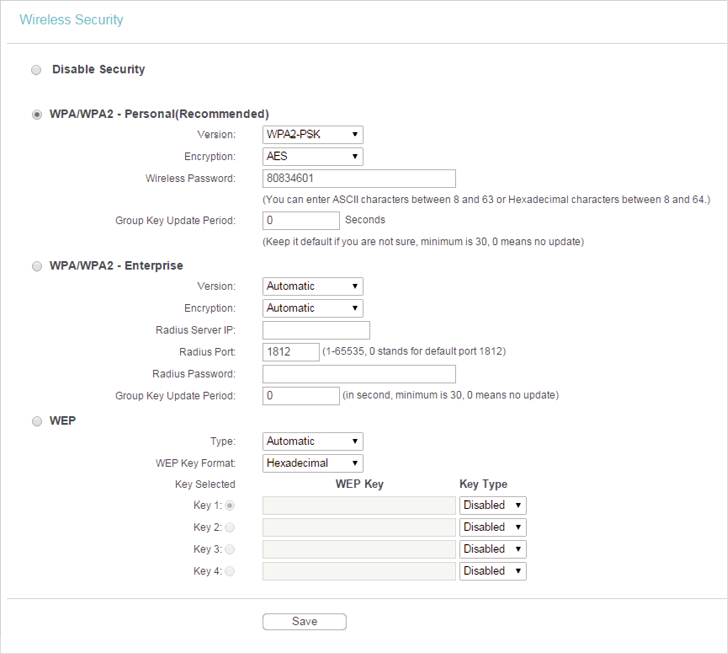
•Disable Security - The wireless security function can be enabled or disabled. If disabled, wireless clients can connect to the router without a password. It’s strongly recommended to choose one of the following modes to enable security.
•WPA-PSK/WPA2-Personal - It’s the WPA/WPA2 authentication type based on pre-shared passphrase.
•Version - Select Automatic, WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK.
•Encryption - Select Automatic, TKIP or AES.
•Wireless Password - Enter ASCII or Hexadecimal characters. For Hexadecimal, the length should be between 8 and 64 characters; for ASCII, the length should be between 8 and 63 characters.
•Group Key Update Period - Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value can be 0 or at least 30. Enter 0 to disable the update.
•WPA /WPA2-Enterprise - It’s based on Radius Server.
•Version - Select Automatic, WPA or WPA2.
•Encryption - Select Automatic, TKIP or AES.
•Radius Server IP - Enter the IP address of the Radius server.
•Radius Port - Enter the port that Radius server used.
•Radius Password - Enter the password for the Radius server.
•Group Key Update Period - Specify the group key update interval in seconds. The value should be 30 or above. Enter 0 to disable the update.
•WEP - It is based on the IEEE 802.11 standard.
•Type - The default setting is Automatic, which can select Shared Key or Open System authentication type automatically based on the wireless client’s capability and request.
•WEP Key Format - Hexadecimal and ASCII formats are provided here. Hexadecimal format stands for any combination of hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f, A-F) in the specified length. ASCII format stands for any combination of keyboard characters in the specified length.
•WEP Key (Password) - Select which of the four keys will be used and enter the matching WEP key. Make sure these values are identical on all wireless clients in your network.
•Key Type - Select the WEP key length (64-bit, 128-bit or 152-bit) for encryption. Disabled means this WEP key entry is invalid.
•64-bit - Enter 10 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-f and A-F. Null key is not permitted) or 5 ASCII characters.
•128-bit - Enter 26 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-f and A-F. Null key is not permitted) or 13 ASCII characters.
•152-bit - Enter 32 hexadecimal digits (any combination of 0-9, a-f and A-F. Null key is not permitted) or 16 ASCII characters.
4.3. Wireless MAC Filtering
Wireless MAC Filtering is used to deny or allow specific wireless client devices to access your network by their MAC addresses.
I want to:
Deny or allow specific wireless client devices to access my network by their MAC addresses.
For example, you want the wireless client A with the MAC address 00-0A-EB-B0-00-0B and the wireless client B with the MAC address 00-0A-EB-00-07-5F to access the router, but other wireless clients cannot access the router
How can I do that?
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Wireless MAC Filtering.
3.Click Enable to enable the Wireless MAC Filtering function.
4.Select Allow the stations specified by any enabled entries in the list to access as the filtering rule.
5.Delete all or disable all entries if there are any entries already.
6.Click Add New and fill in the blank.
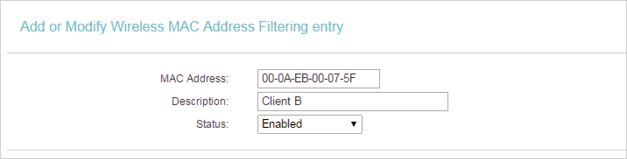
1 )Enter the MAC address 00-0A-EB-B0-00-0B/00-0A-EB-00-07-5F in the MAC Address field.
2 )Enter wireless client A/B in the Description field.
3 )Leave the status as Enabled.
4 )Click Save and click Back.
7.The configured filtering rules should be listed as the picture shows below.
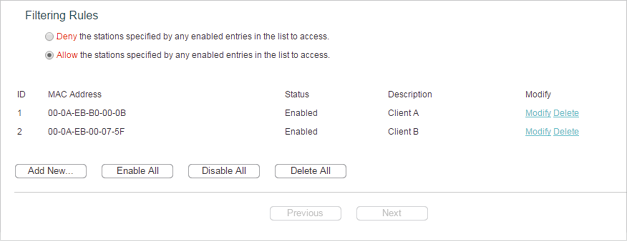
Done!
Now only client A and client B can access your network.
4.4. Wireless Advanced
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Wireless Advanced.
3.Configure the advanced settings of your wireless network and click Save.
Note:
If you are not familiar with the setting items on this page, it’s strongly recommended to keep the provided default values; otherwise it may result in lower wireless network performance.
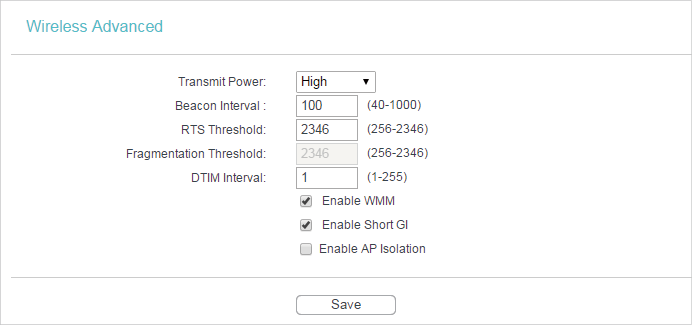
•Transmit Power - Select High, Middle or Low which you would like to specify for the router. High is the default setting and recommended.
•Beacon Interval - Enter a value between 40-1000 milliseconds for Beacon Interval here. Beacon Interval value determines the time interval of the beacons. The beacons are the packets sent by the Router to synchronize a wireless network. The default value is 100.
•RTS Threshold - Here you can specify the RTS (Request to Send) Threshold. If the packet is larger than the specified RTS Threshold size, the Router will send RTS frames to a particular receiving station and negotiate the sending of a data frame. The default value is 2346.
•Fragmentation Threshold - This value is the maximum size determining whether packets will be fragmented. Setting a low value for the Fragmentation Threshold may result in poor network performance because of excessive packets. 2346 is the default setting and is recommended.
•DTIM Interval - This value determines the interval of the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM). A DTIM field is a countdown field informing clients of the next window for listening to broadcast and multicast messages. When the Router has buffered broadcast or multicast messages for associated clients, it sends the next DTIM with a DTIM Interval value. You can specify the value between 1-255 Beacon Intervals. The default value is 1, which indicates the DTIM Interval is the same as Beacon Interval.
•Enable WMM - WMM function can guarantee the packets with high-priority messages being transmitted preferentially. It is strongly recommended to enable this function.
•Enable Short GI - It is recommended to enable this function, for it will increase the data capacity by reducing the guard interval time.
•Enable AP Isolation - This function isolates all connected wireless stations so that wireless stations cannot access each other through WLAN. This function will be disabled if WDS/Bridge is enabled.
4.5. Wireless Statistics
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Wireless Statistics to check the data packets sent and received by each client device connected to the router.
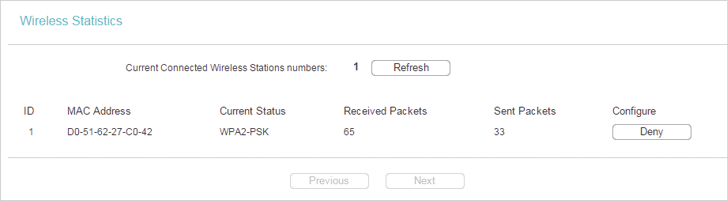
•MAC Address - The MAC address of the connected wireless client.
•Current Status - The running status of the connected wireless client.
•Received Packets - Packets received by the wireless client.
•Sent Packets - Packets sent by the wireless client.
•Configure - The button is used for loading the item to the Wireless MAC Filtering list.
•Allow - If the Wireless MAC Filtering function is enabled, click this button to allow the client to access your network.
•Deny - If the Wireless MAC Filtering function is enabled, click this button to deny the client to access your network.
4.6. Throughput Monitor
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to Wireless > Throughput Monitor to view the wireless throughput information.
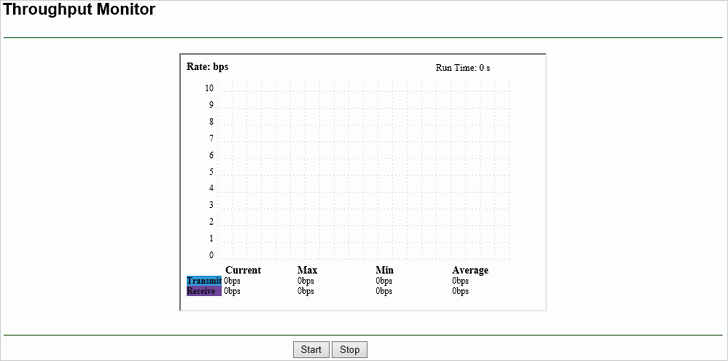
•Rate - The unit for the Throughput.
•Run Time - How long Throughput Monitor runs.
•Transmit - Wireless transmit rate information.
•Receive - Wireless receive rate information.
Click Start / Stop to start or stop wireless throughput monitor.
By default, the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server is enabled and the router acts as a DHCP server; it dynamically assigns TCP/IP parameters to client devices from the IP Address Pool. You can change the settings of DHCP Server if necessary, and you can reserve LAN IP addresses for specified client devices.
5.1. DHCP Settings
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to DHCP > DHCP Settings.
3.Specify DHCP server settings and click Save.
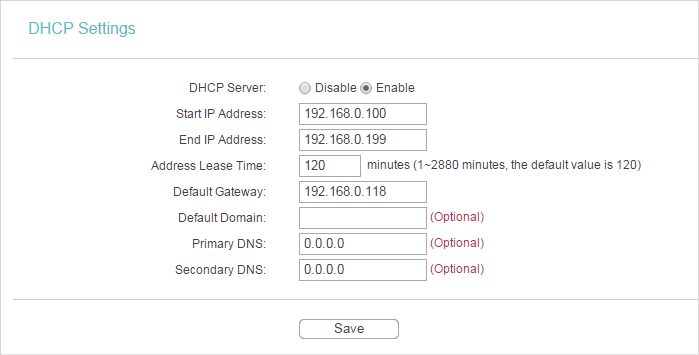
•DHCP Server - Enable or disable the DHCP server. If disabled, you must have another DHCP server within your network or else you must configure the computer manually.
•Start IP Address - Specify an IP address for the DHCP Server to start with when assigning IP addresses. 192.168.0.100 is the default start address.
•End IP Address - Specify an IP address for the DHCP Server to end with when assigning IP addresses. 192.168.0.199 is the default end address.
•Address Lease Time - The Address Lease Time is the amount of time a network user will be allowed to connect to the router with the current dynamic IP Address. When time is up, the user will be automatically assigned a new dynamic IP address. The range of the time is 1 ~ 2880 minutes. The default value is 120.
•Default Gateway (Optional) - It is suggested to input the IP address of the LAN port of the router. The default value is 192.168.0.254.
•Default Domain (Optional) - Input the domain name of your network.
•Primary DNS (Optional) - Input the DNS IP address provided by your ISP.
•Secondary DNS (Optional) - Input the IP address of another DNS server if your ISP provides two DNS servers.
Note:
•To use the DHCP server function of the router, you must configure all computers on the LAN as Obtain an IP Address automatically.
•When you choose Static IP in Network > LAN, the DHCP Server function will be disabled.
5.2. DHCP Client List
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to DHCP > DHCP Client List to view the information of the clients connected to the router.
•Client Name - The name of the DHCP client.
•MAC Address - The MAC address of the DHCP client.
•Assigned IP - The IP address that the router has allocated to the DHCP client.
•Lease Time - The time of the DHCP client leased. After the dynamic IP address has expired, a new dynamic IP address will be automatically assigned to the user.
You cannot change any of the values on this page. To update this page and show the current attached devices, click Refresh.
5.3. Address Reservation
You can reserve an IP address for a specific client. When you specify a reserved IP address for a PC on the LAN, this PC will always receive the same IP address each time when it accesses the DHCP server.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to DHCP > Address Reservation.
3.Click Add New and fill in the blank.
1 )Enter the MAC address (in XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX format) of the client for which you want to reserve an IP address.
2 )Enter the IP address (in dotted-decimal notation) which you want to reserve for the client.
3 )Leave the status as Enabled.
4 )Click Save.
6.1. Diagnostic
Diagnostic is used to test the connectivity between the router and the host or other network devices.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Diagnostic.
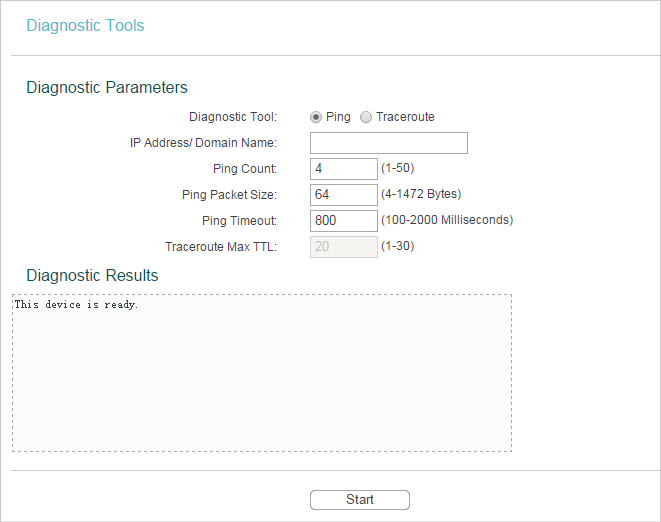
•Diagnostic Tool - Select one diagnostic tool.
•Ping - This diagnostic tool troubleshoots connectivity, reachability, and name resolution to a given host or gateway.
•Tracerouter - This diagnostic tool tests the performance of a connection.
Note:
You can use ping/traceroute to test both numeric IP address or domain name. If pinging/tracerouting the IP address is successful, but pinging/tracerouting the domain name is not, you might have a name resolution problem. In this case, ensure that the domain name you are specifying can be resolved by using Domain Name System (DNS) queries.
•IP Address/Domain Name - Enter the destination IP address (such as 192.168.0.1) or Domain name (such as www.tp-link.com).
•Pings Count - The number of Ping packets for a Ping connection.
•Ping Packet Size - The size of Ping packet.
•Ping Timeout - Set the waiting time for the reply of each Ping packet. If there is no reply in the specified time, the connection is overtime.
•Traceroute Max TTL - The max number of hops for a Traceroute connection.
3.Click Start to check the connectivity of the internet.
4.The Diagnostic Results page displays the diagnosis result. If the result is similar to the following figure, the connectivity of the internet is fine.
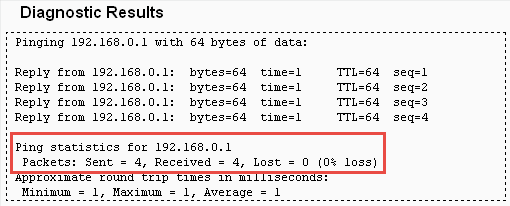
Note:
Only one user can use this tool at one time. Options “Number of Pings”, “Ping Size” and “Ping Timeout” are used for the Ping function. Option “Tracert Hops” is used for the Tracert function.
6.2. Ping Watch Dog
The Ping Watch Dog is dedicated for continuous monitoring of the particular connection to remote host using the Ping tool. It makes the router continuously ping a user defined IP address (it can be the internet gateway for example). If it is unable to ping under the user defined constraints, the router will automatically reboot.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Ping Watch Dog. Configure the settings and click Save.
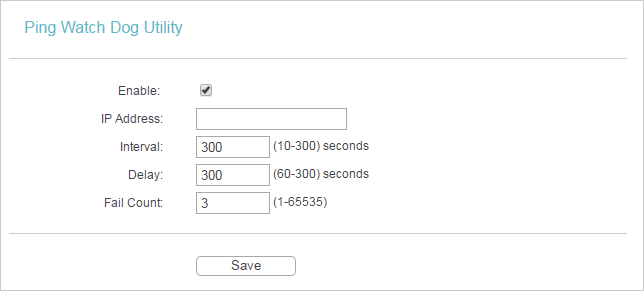
•Enable - Turn on/off Ping Watch Dog.
•IP Address - The IP address of the target host where the Ping Watch Dog Utility is sending ping packets.
•Interval - Time interval between two ping packets which are sent out continuously.
•Delay - Time delay before first ping packet is sent out when the router is restarted.
•Fail Count - Upper limit of the ping packets the router can drop continuously. If this value is overrun, the router will restart automatically.
6.3. Firmware Upgrade
TP-Link is dedicated to improving and richening the product features, giving users a better network experience. We will release the latest firmware at TP-Link official website. You can download the latest firmware file from the Support page of our website
www.tp-link.com and upgrade the firmware to the latest version.
1.Download the latest firmware file for the router from our website www.tp-link.com.
2.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
3.Go to System Tools > Firmware Upgrade.
4.Click Browse to locate the downloaded firmware file, and click Upgrade.
6.4. Factory Defaults
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Factory Defaults. Click Restore to reset all settings to the default values.
•The default Username: admin
•The default Password: admin
•The default IP Address: 192.168.0.254
•The default Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
6.5. Backup & Restore
The configuration settings are stored as a configuration file in the router. You can backup the configuration file in your computer for future use and restore the router to the previous settings from the backup file when needed.
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Backup & Restore.
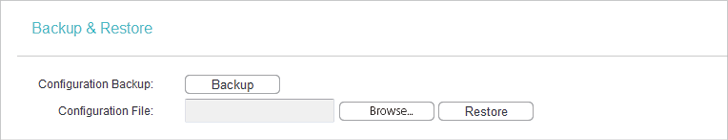
•To backup configuration settings:
Click Backup to save a copy of the current settings in your local computer. A “.bin“ file of the current settings will be stored in your computer.
•To restore configuration settings:
1.Click Choose File to locate the backup configuration file stored in your computer, and click Restore.
2.Wait a few minutes for the restoring and rebooting.
Note: During the restoring process, do not power off or reset the router.
6.6. Reboot
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Reboot, and you can restart your router.
Some settings of the router will take effect only after rebooting, including:
•Change the LAN IP Address (system will reboot automatically).
•Change the DHCP Settings.
•Change the Working Modes.
•Change the Web Management Port.
•Upgrade the firmware of the router (system will reboot automatically).
•Restore the router to its factory defaults (system will reboot automatically).
•Update the configuration with the file (system will reboot automatically).
6.7. Password
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > Password, and you can change the factory default username and password of the router.
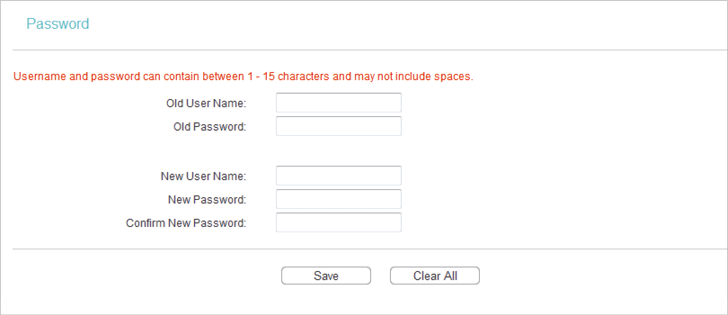
It is strongly recommended that you change the default username and password of the router, for all users that try to access the router’s web management page or Quick Setup will be prompted for the router’s username and password.
Note:
The new username and password must not exceed 15 characters and not include any spacing.
3.Click Save.
6.8. System Log
1.Visit http://tplinkwifi.net, and log in with the username and password you set for the router.
2.Go to System Tools > System Log, and you can view the logs of the router.
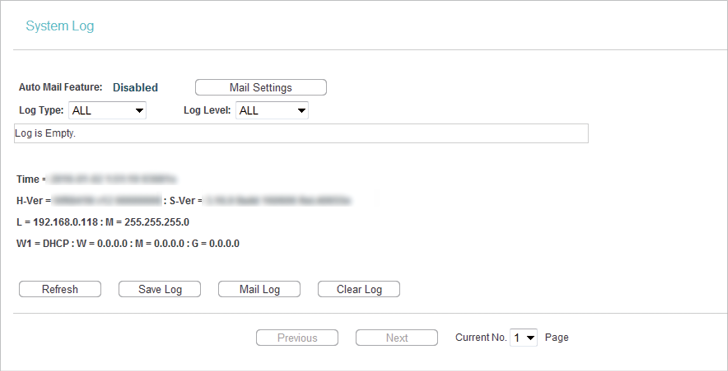
•Auto Mail Feature - Indicates whether the auto mail feature is enabled or not.
•Mail Settings - Set the receiving and sending mailbox address, server address, validation information as well as the timetable for Auto Mail Feature.
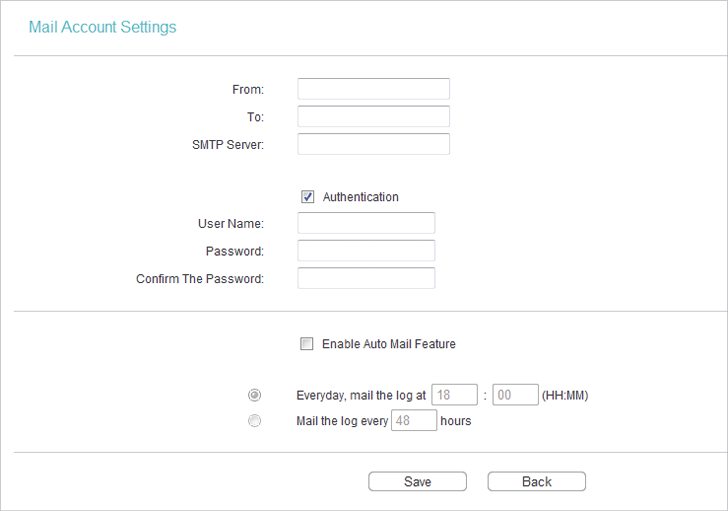
•From - Your mail box address. The router will connect it to send logs.
•To - Recipient’s mail address. The destination mailbox which will receive logs.
•SMTP Server - Your smtp server. It corresponds with the mailbox filled in the From field. You can log in to the relevant website for help if you are not clear with the address.
•Authentication - Most SMTP Server requires Authentication. It is required by most mailboxes that need user name and password to log in.
Note:
Only when you select Authentication, do you have to enter the user name and password in the following fields.
•User Name - Your mail account name filled in the From field. The part behind @ is included.
•Password - Your mail account password.
•Confirm The Password - Enter the password again to confirm.
•Enable Auto Mail Feature - Select it to mail logs automatically. You could mail the current logs either at a specified time everyday or by intervals, but only one could be the current effective rule. Enter the desired time or intervals in the corresponding field.
Click Save to apply your settings.
Click Back to return to the previous page.
•Log Type - By selecting the log type, only logs of this type will be shown.
•Log Level - By selecting the log level, only logs of this level will be shown.
•Refresh - Refresh the page to show the latest log list.
•Save Log - Click to save all the logs in a “txt” file.
•Mail Log - Click to send an email of current logs manually according to the address and validation information set in Mail Settings.
•Clear Log - All the logs will be deleted from the router permanently, not just from the page.
Click Next to go to the next page, or click Previous to return to the previous page.
Click Logout at the bottom of the main menu, and you will log out of the web page and return to the login window.